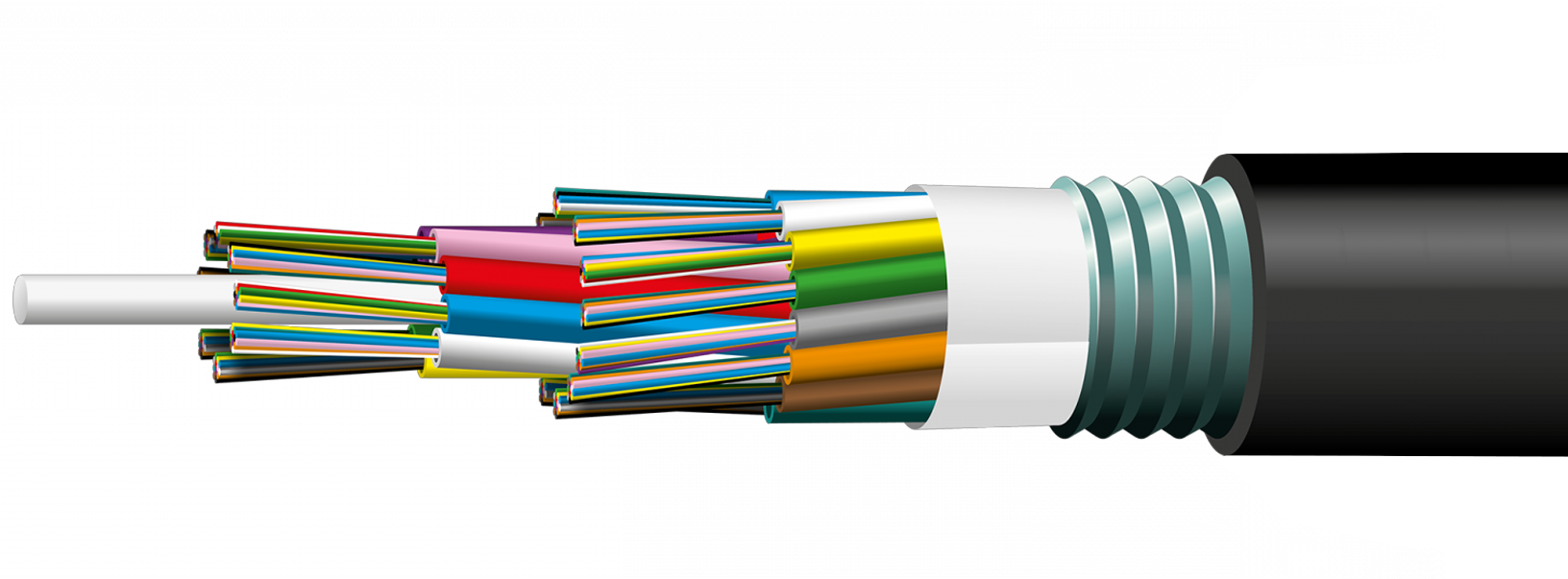
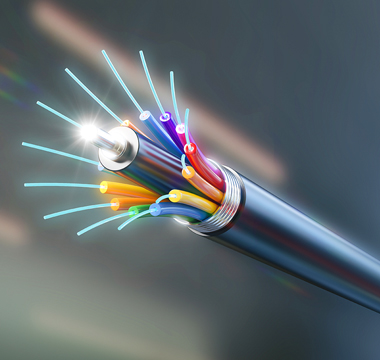
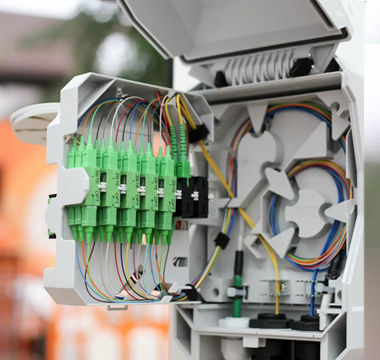
Fiber Optics Applications
A range of industries use fiber optic cables for reliable and fast connectivity.
Data Centre Solutions: Networking and broadcasting
Fiber optics are crucial in computer networking and broadcasting within data centers. Their high data transmission rates and extensive bandwidth capabilities make them ideal for networking, ensuring efficient and reliable connectivity. Additionally, fiber optics are widely used in broadcasting and electronics, enhancing connections and overall performance.
Internet and cable television
Fiber optics are commonly used for both internet and cable television connections. They can be installed to support long-distance connections between computer networks located in different places.
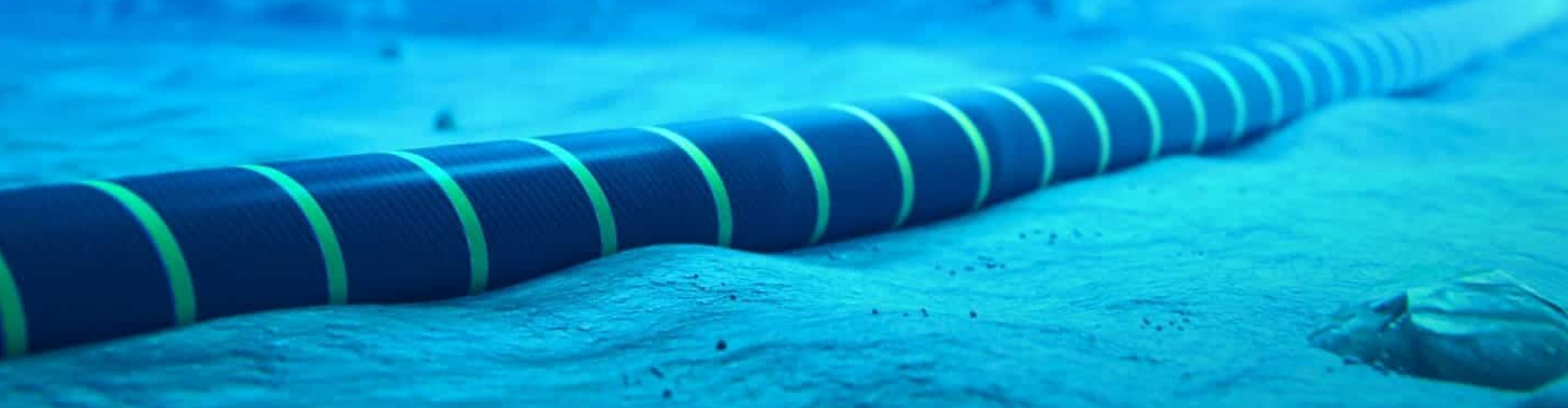
Undersea environments
Fiber optic cables are utilized in environments that are more vulnerable, such as undersea cables, because they can be submerged in water and require less frequent replacement.
Military and space
Optical fiber is employed by the military and space industries for communication and signal transmission, as well as for temperature sensing. Its lighter weight and smaller size make fiber optic cables advantageous in these sectors.
Medical
Fiber optics play a crucial role in various medical instruments, providing precise illumination and enabling biomedical sensors that assist in minimally invasive procedures. Optical fiber's immunity to electromagnetic interference makes it particularly suitable for tests like MRI scans. Medical applications of fiber optics also include X-ray imaging, endoscopy, light therapy, and surgical microscopy.
 The Most Cutting-EdgeFIBER OPTIC SOLUTIONSConnect with us for more
The Most Cutting-EdgeFIBER OPTIC SOLUTIONSConnect with us for more The latest and most advancedFIBER OPTIC PRODUCTSCheck out our range of products
The latest and most advancedFIBER OPTIC PRODUCTSCheck out our range of products We support your fiber optic solutionsCONSULTATION AND SYSTEM INTEGRATIONThe best and most skilled team of experts
We support your fiber optic solutionsCONSULTATION AND SYSTEM INTEGRATIONThe best and most skilled team of experts